Image search has quietly become one of the most powerful - and most misunderstood - tools on the internet.
People don’t just look at images anymore. They search with them, verify truth through them, buy products from them, and discover brands because of them. From Google Images and Google Lens to reverse image search engines and AI-powered visual recognition, image search has evolved far beyond typing keywords into a box.
This guide goes deeper than surface-level explanations. It shows how image search actually works, how professionals use it in real scenarios, and how you can leverage image search techniques for SEO, research, verification, and growth — all explained in plain, human language.
Table of Contents:
- What Is Image Search (And Why It Matters More Than Ever)
- How Image Search Engines Actually Understand Images
- Types of Image Search Techniques (Explained Simply)
- Reverse Image Search: Real-World Uses Most Guides Miss
- Visual Similarity & AI-Driven Image Discovery
- Object Recognition, OCR & Contextual Search
- Best Image Search Tools (With Practical Use Cases)
- Image Search Techniques for SEO & Organic Traffic
- Image Optimization for Search Engines (Advanced Checklist)
- Image Search for Research, Verification & Brand Protection
- Common Image Search Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
- The Future of Image Search
- Final Thoughts
1. What Is Image Search (And Why It Matters More Than Ever)
Image search is the process of finding information through images, not just about images.
Instead of relying only on words, image search engines analyze visual signals - shapes, colors, objects, text inside images, and surrounding context — to understand what an image represents.
Today, image search is used to:
- Discover products without knowing their names
- Verify if an image is real, edited, or stolen
- Find the original source of viral visuals
- Drive organic traffic through Google Images
- Identify places, objects, people, and text instantly
With platforms like Google reporting billions of visual searches per month, image search is no longer optional - it’s foundational.
2. How Image Search Engines Actually Understand Images
Most guides oversimplify this part. Image search does not rely on one factor — it’s a layered system.
Core Signals Used by Image Search Engines
- Visual Data
- Shapes
- Colors
- Patterns
- Edges
- Objects and faces
- Metadata
- File name
- Alt text
- EXIF data (camera, date, location)
- Captions
- Contextual Content
- Surrounding text
- Headings
- Page topic
- Internal links
- User Interaction Signals
- Click-through rate
- Engagement
- Bounce behavior
Search engines blend computer vision + machine learning + context analysis to decide where an image belongs.
This is why image SEO is never just “add alt text” - it’s about alignment.
3. Types of Image Search Techniques (Explained Simply)
There isn’t just one kind of image search. Each method serves a different purpose.
A. Text-Based Image Search
This is the most familiar method: typing keywords like “modern home office setup” into Google Images.
Search engines match your query against:
- Alt text
- File names
- Captions
- Page content
Best used for:
Discovery, inspiration, general browsing, SEO traffic

![]()
![]()
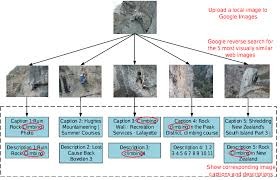
B. Reverse Image Search
Reverse image search flips the process. Instead of typing words, you upload an image or paste its URL.
The engine then finds:
- Exact matches
- Cropped or edited versions
- Pages where the image appears
Best used for:
- Finding original sources
- Image theft detection
- Fact-checking
- Brand monitoring
![]()
![]()
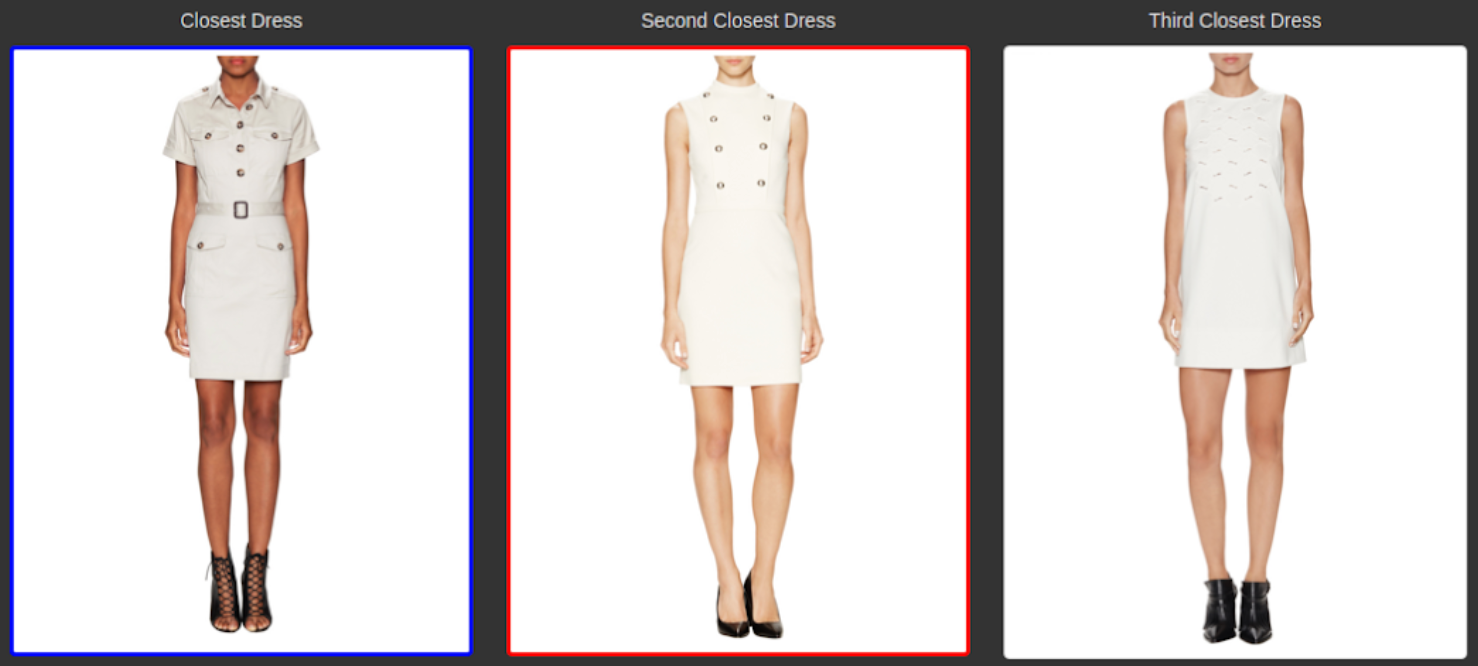
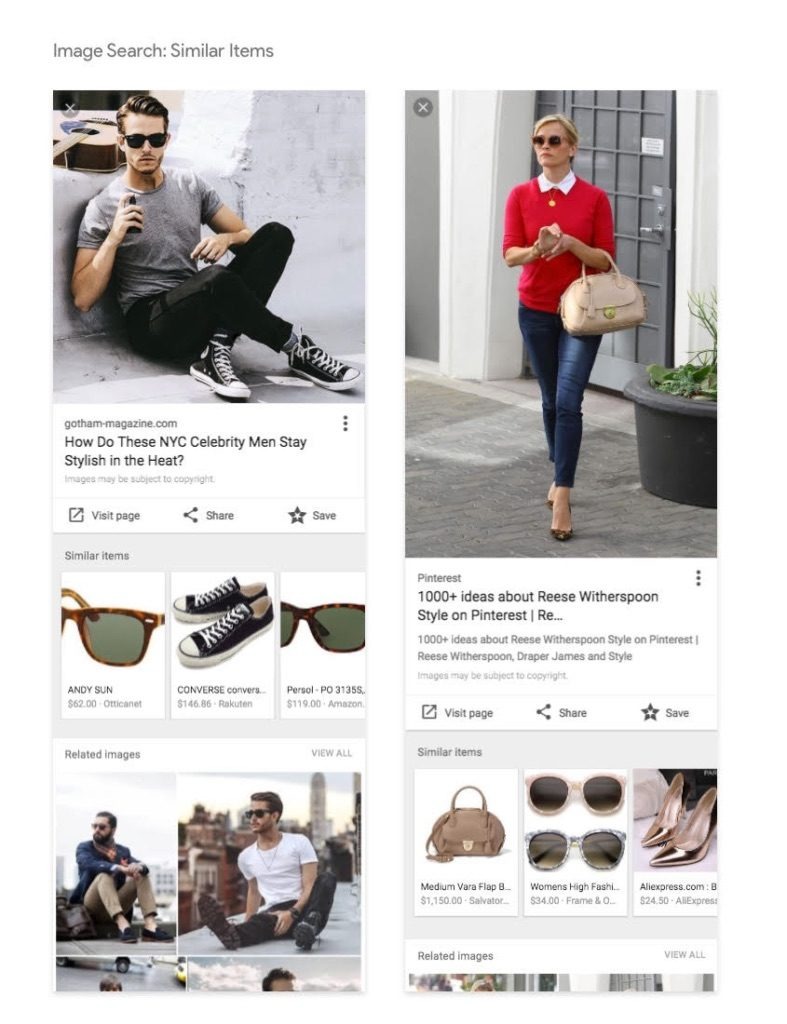
C. Visual Similarity Search
This technique finds images that look similar, not identical.
Example:
You upload a chair image → the engine shows chairs with similar shapes, colors, or styles.
This is heavily used in:
- Fashion
- Home decor
- eCommerce
- Product discovery
![]()
![]()
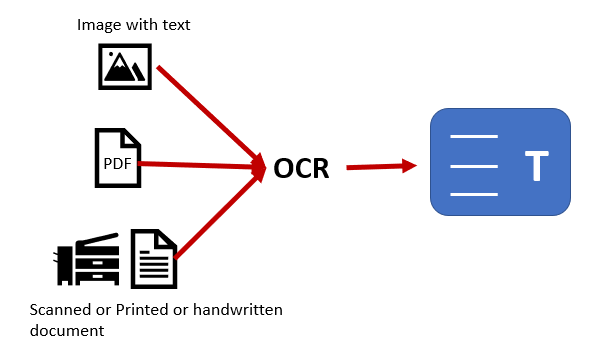
D. Object Recognition & OCR Search
Advanced tools can:
- Identify objects (plants, animals, tools)
- Read text inside images (OCR)
- Recognize landmarks and products
This is where tools like Google Lens dominate.
![]()
![]()
4. Reverse Image Search: Real-World Uses Most Guides Miss
Reverse image search is not just for curiosity - professionals use it daily.
1. SEO & Link Building
Upload your original images and find websites using them without attribution. Politely request a backlink - this is one of the highest-quality white-hat link strategies.
2. Content Verification
Journalists and researchers use reverse image search to see:
- When an image first appeared
- Whether it’s recycled from older events
- If it’s been manipulated
3. Brand Protection
Brands monitor logo misuse, fake ads, and impersonation using reverse image search.
5. Visual Similarity & AI-Driven Image Discovery
Similarity search relies heavily on AI models trained on billions of images.
These systems recognize:
- Object geometry
- Color distribution
- Texture
- Spatial relationships
This allows discovery without language barriers, which is why visual search adoption is exploding in mobile commerce.
Pinterest, Google, and Bing all invest heavily here - because people don’t always know the words for what they want.
6. Object Recognition, OCR & Contextual Search
Modern image search goes beyond visuals.
OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
- Extracts text from screenshots, documents, signs
- Allows searching text inside images
- Extremely useful for research and archiving
Contextual Understanding
Engines combine image content with:
- Location data
- Time
- Page topic
- User intent
This is why the same image can rank differently on different pages.
7. Best Image Search Tools (With Practical Use Cases)
|
Tool |
Best For |
|
Google Images |
SEO, discovery, general search |
|
Google Lens |
Object recognition, OCR, shopping |
|
Bing Visual Search |
Product matching |
|
TinEye |
Original source tracking |
|
Yandex Images |
Face recognition accuracy |
Pro tip: Always use at least two tools - no single engine has full coverage.
8. Image Search Techniques for SEO & Organic Traffic
Image search is an underused traffic channel.
Well-optimized images can:
- Rank independently in Google Images
- Appear in featured snippets
- Increase page dwell time
- Improve topical relevance
Google treats images as supporting evidence for content quality.
9. Image Optimization for Search Engines (Advanced Checklist)
Technical Optimization
- Descriptive file names (not IMG_1234.jpg)
- WebP or AVIF formats
- Proper dimensions
- Lazy loading
On-Page Optimization
- Contextual alt text (not keyword stuffing)
- Relevant captions
- Images placed near related text
- Schema markup (ImageObject, FAQ)
Experience Signals
- Original visuals (screenshots, diagrams)
- Helpful annotations
- Mobile-friendly display
This is where Experience (E) in E-E-A-T truly shines.
10. Image Search for Research, Verification & Brand Protection
Image search is critical in:
- Fact-checking misinformation
- Tracking viral image origins
- Verifying AI-generated visuals
- Protecting intellectual property
In a world of deepfakes and AI images, image verification is no longer optional.
11. Common Image Search Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
- Assuming top result = original
- Ignoring image context
- Using stock images exclusively
- Over-optimizing alt text
- Forgetting mobile image experience
Each of these weakens trust and rankings.
12. The Future of Image Search
Image search is moving toward:
- Multimodal AI (text + image + voice)
- Real-time camera-based search
- AI-generated image detection
- Personalized visual discovery
Search engines are shifting from matching to understanding.
13. Final Thoughts
Image search techniques are no longer “advanced SEO tricks” - they’re core digital skills.
When used correctly, image search helps you:
- Rank in visual SERPs
- Build authority and trust
- Verify information accurately
- Protect and monetize your content
- Meet users where language fails
If text search is about answers, image search is about understanding - and the brands that master it now will dominate visibility in the years ahead.
FAQs:
1. What are image search techniques?
Image search techniques are methods used to find information using images instead of text. These include text-based image search, reverse image search, visual similarity search, object recognition, and OCR-based search.
2. How does reverse image search work?
Reverse image search works by analyzing the visual elements of an image—such as shapes, colors, and patterns—and matching them against indexed images across the web to find exact or similar results.
3. What is the difference between reverse image search and visual search?
Reverse image search finds exact or near-exact matches of an image, while visual search focuses on finding visually similar images even if they are different files or variations.
4. Can image search help with SEO?
Yes, image search can significantly improve SEO by driving traffic from Google Images, increasing content relevance, improving user engagement, and helping pages rank for visual-based queries.
5. How do I optimize images for search engines?
Images can be optimized by using descriptive file names, relevant alt text, proper compression, modern formats like WebP, contextual placement, and structured data such as ImageObject schema.
6. What tools are best for image search?
Popular image search tools include Google Images, Google Lens, Bing Visual Search, TinEye, and Yandex Images. Using more than one tool provides better coverage and accuracy.
7. How can I find the original source of an image?
You can find the original source by using reverse image search tools and filtering results by date or earliest indexed appearance.
8. Is reverse image search accurate?
Reverse image search is highly accurate for popular or widely shared images but may be limited for new, low-resolution, or heavily edited visuals.
9. Can image search detect fake or edited images?
Image search can help detect fake or reused images by revealing older versions, different contexts, or signs of manipulation, but it should be combined with other verification methods.
10. Does Google rank images separately from web pages?
Yes, images are indexed and ranked separately in Google Images, but their performance is strongly influenced by the quality and relevance of the page they appear on.
11. Is image search useful for eCommerce?
Absolutely. Image search allows users to find products visually, compare similar items, and discover brands without knowing product names, which improves conversion rates.
12. Can text inside images be searched?
Yes, modern image search engines use OCR (Optical Character Recognition) to read and index text found inside images, screenshots, and documents.
