GPU as a Service: On-Demand Cloud GPUs for AI, ML & HPC
GPU as a Service (GPUaaS) is a cloud computing model that delivers on-demand access to high-performance Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) over the internet. Instead of purchasing and maintaining expensive GPU hardware, organizations can rent GPU resources from a cloud provider and scale them up or down based on workload needs.
GPU as a Service is widely used for artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), deep learning, high-performance computing (HPC), data analytics, and graphics-intensive workloads.
How GPU as a Service Works
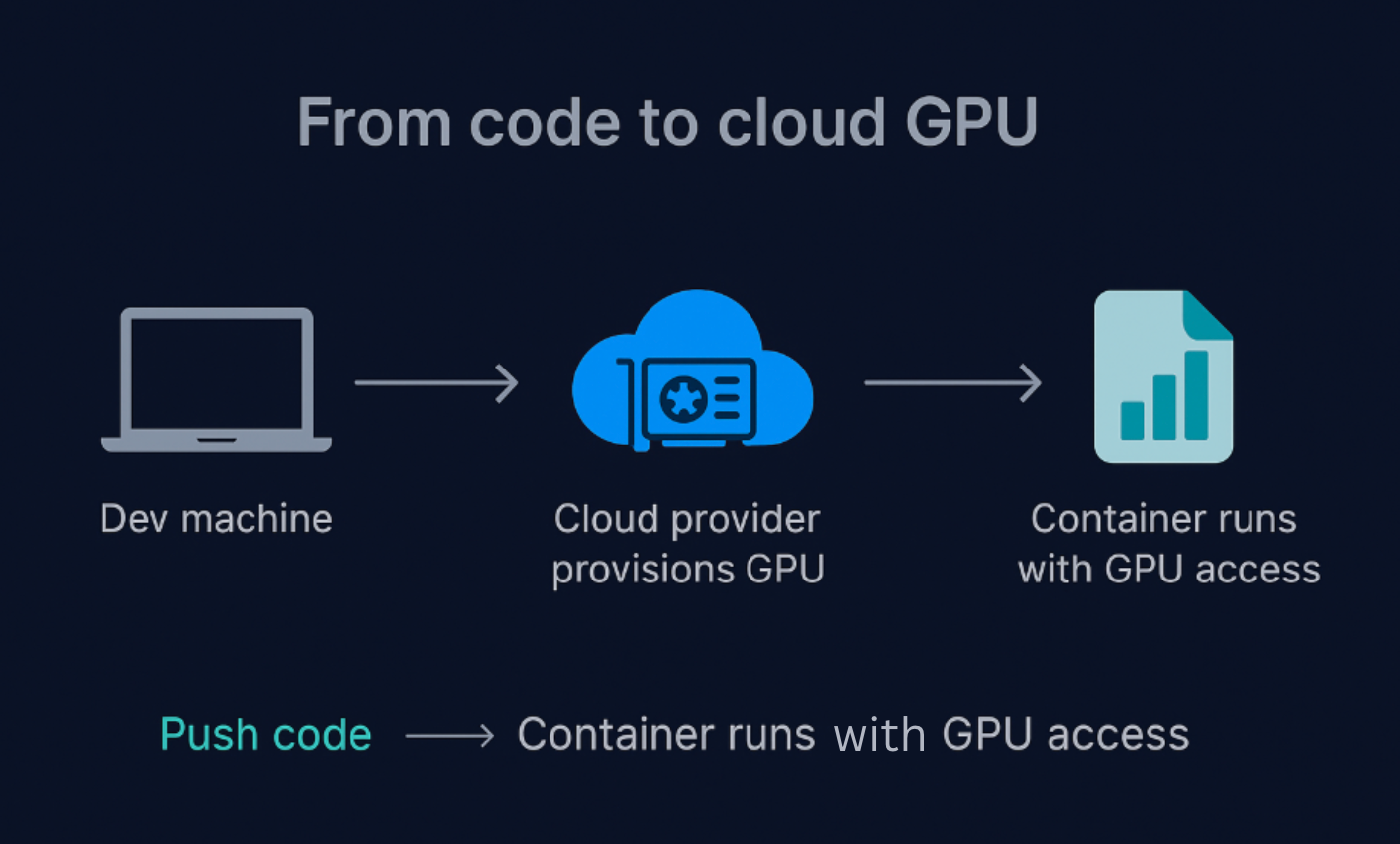
GPUaaS operates through a virtualized cloud infrastructure:
- GPU Hardware Pool – High-end GPUs (e.g., NVIDIA H100, A100, L40) are hosted in provider data centers.
- Virtualization Layer – GPUs are partitioned or allocated using virtualization or container technologies.
- Cloud Access – Customers access GPUs via APIs, consoles, or orchestration tools.
- Pay-as-You-Go Billing – Charges are based on usage (per hour, per second, or per workload).
This model eliminates hardware procurement delays and allows rapid experimentation and scaling.
Key Features of GPU as a Service
- On-demand GPU provisioning
- Elastic scalability for burst workloads
- Multi-tenant or dedicated GPU options
- Integration with AI/ML frameworks (TensorFlow, PyTorch, CUDA)
- Secure cloud access with enterprise-grade compliance
- Global availability through distributed data centers
Benefits of GPU as a Service
1. Cost Efficiency
Avoid high upfront capital expenditure on GPUs, cooling, power, and maintenance.
2. Faster Time to Market
Provision GPUs in minutes instead of weeks or months.
3. Scalability on Demand
Scale from a single GPU to thousands for large training jobs.
4. Access to Latest GPU Technology
Always use next-generation GPUs without refresh cycles.
5. Operational Simplicity
No need to manage drivers, firmware, or physical infrastructure.
GPUaaS vs CPU-Based Cloud Computing
|
Feature |
GPUaaS |
CPU Cloud |
|
Processing Model |
Massively parallel |
Sequential / limited parallel |
|
AI & ML Training |
Excellent |
Poor to moderate |
|
Cost per Compute |
Higher per hour |
Lower per hour |
|
Performance per Dollar |
Very high |
Lower for AI workloads |
|
Best Use Cases |
AI, ML, HPC, rendering |
Web apps, databases |
Common Use Cases for GPU as a Service
Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
- Model training and fine-tuning
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- Computer vision and image recognition
High-Performance Computing (HPC)
- Scientific simulations
- Financial risk modeling
- Weather forecasting
Data Analytics
- Large-scale data processing
- Real-time analytics
Media & Graphics
- Video rendering
- 3D modeling
- Gaming and AR/VR workloads
GPU as a Service Deployment Models
- Public Cloud GPUaaS – Shared infrastructure, highly scalable
- Private GPUaaS – Dedicated GPUs for regulated workloads
- Hybrid GPUaaS – Combination of on-premise and cloud GPUs
- Edge GPUaaS – Low-latency processing at edge locations
Security and Compliance in GPUaaS
Enterprise-grade GPUaaS platforms offer:
- Network isolation and encryption
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Compliance with ISO, SOC, GDPR, HIPAA (depending on provider)
- Secure workload isolation between tenants
Challenges of GPU as a Service
- Cost management for long-running workloads
- Data gravity and transfer latency
- Limited GPU availability during peak demand
- Vendor lock-in if using proprietary tooling
Mitigation strategies include workload scheduling, hybrid deployments, and cost-optimization policies.
How to Choose the Right GPUaaS Provider
Key evaluation criteria:
- GPU types and performance benchmarks
- Global data center coverage
- Pricing transparency
- AI/ML ecosystem compatibility
- Network performance and latency
- SLA and enterprise support
GPU as a Service in Enterprise Cloud Strategy
Leading providers such as Tata Communications position GPUaaS as a foundational layer for AI-ready cloud infrastructure, enabling enterprises to modernize workloads without re-architecting data centers.
GPUaaS increasingly integrates with cloud networking, edge computing, and hybrid cloud platforms to support real-time and data-intensive AI applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is GPUaaS used for?
GPUaaS is used for AI/ML training, inference, HPC workloads, data analytics, and graphics rendering.
Is GPU as a Service expensive?
While GPUs cost more per hour than CPUs, they significantly reduce total compute time—often lowering overall costs.
Can GPUaaS be used for production workloads?
Yes. Many enterprises run mission-critical AI and analytics workloads on GPUaaS platforms.
What is the difference between GPUaaS and on-prem GPUs?
GPUaaS offers elasticity, global reach, and operational simplicity, while on-prem GPUs require capital investment and maintenance.
Summary
GPU as a Service (GPUaaS) enables organizations to access high-performance GPU computing without infrastructure complexity, accelerating AI innovation and data-driven workloads. As AI adoption grows, GPUaaS is becoming a core component of modern cloud and enterprise IT strategies.
