What is Object Storage and How Does It Work?
In the era of cloud computing, businesses generate and store massive amounts of data every day. Managing this data efficiently, securely, and cost-effectively is critical. Object storage has emerged as a leading solution for storing unstructured data at scale.
In this article, we’ll explore what object storage is, how it works, its benefits, and key use cases for modern enterprises.
What is Object Storage?
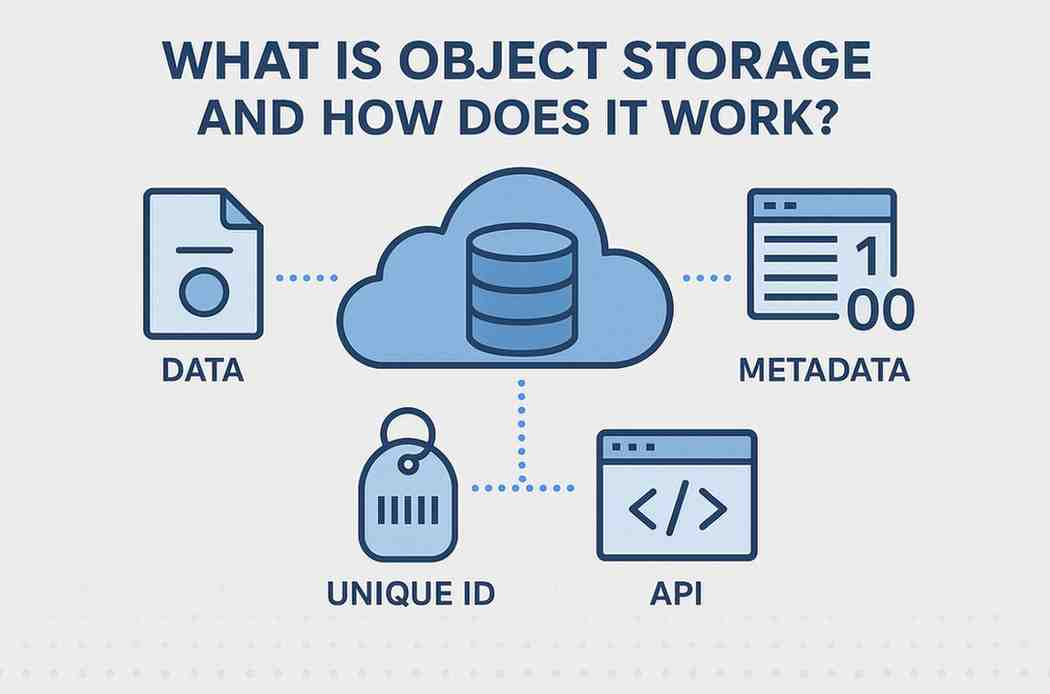
Object storage is a method of storing data as discrete units called objects, rather than in traditional file systems or block storage. Each object contains:
- Data – The actual file or content being stored.
- Metadata – Information describing the object, such as file type, creation date, access permissions, and custom tags.
- Unique Identifier (ID) – A globally unique identifier used to retrieve the object.
Unlike traditional storage methods, object storage does not rely on a hierarchical structure (folders and directories). Instead, it stores data in a flat, scalable namespace, which allows for virtually unlimited storage capacity.
How Object Storage Works
- Storing Data as Objects – When a file is uploaded, the system converts it into an object. Each object is assigned a unique ID and metadata that describes its properties.
- Flat Namespace – Instead of storing files in folders, all objects exist in a flat structure. This eliminates limitations associated with traditional file systems and allows for easy scaling.
- Metadata Management – Metadata enables advanced search, tagging, and policy enforcement, allowing searches by creation date, owner, or content type.
- Data Retrieval – Objects are accessed using their unique ID rather than a file path, ensuring fast and efficient retrieval even at massive scale.
- Scalability and Distribution – Object storage systems distribute data across multiple nodes or regions, providing redundancy, fault tolerance, and global accessibility.
Key Features of Object Storage
- Scalability – Handles petabytes of data without limitations.
- Durability – Data is replicated across multiple locations to prevent loss.
- Accessibility – Objects can be retrieved via HTTP APIs or cloud SDKs.
- Cost-Effective – Ideal for storing large volumes of infrequently accessed data.
- Metadata-Rich – Facilitates advanced search, indexing, and analytics.
- Integration – Compatible with cloud services, AI pipelines, and big data platforms.
Benefits of Object Storage
- Elastic Scalability – Object storage grows seamlessly as your data grows, with no need to restructure hierarchies.
- High Durability and Reliability – Data is automatically replicated across multiple nodes or regions to protect against failures.
- Cost Efficiency – Pay-as-you-go models allow scalable storage without heavy on-premises investment.
- Global Accessibility – Access data from anywhere, ideal for distributed teams and applications.
- Simplified Management – Metadata-driven architecture simplifies data search and management.
- Supports Modern Workloads – Perfect for unstructured data like images, videos, logs, backups, AI datasets, and IoT data.
Common Use Cases for Object Storage
- Cloud Backups and Archiving – Cost-effective solution for long-term data retention with high durability.
- Media Storage – Store and access video, audio, and images globally at scale.
- AI and Machine Learning Workloads – Provides scalable storage for AI-trained models and large datasets.
- Log Storage and Analytics – Store logs from applications or IoT devices for monitoring and compliance.
- Content Delivery – Ideal for hosting static assets like images, CSS, or JavaScript for fast, scalable delivery.
Object Storage vs Traditional Storage
| Feature | Object Storage | File Storage | Block Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Flat, metadata-driven | Hierarchical | Fixed-size blocks |
| Scalability | Extremely scalable | Limited by server/file system | Scales with block volume |
| Access | HTTP APIs, SDKs | File paths | Direct access via OS |
| Cost | Low for large data | Moderate | High for large datasets |
| Use Cases | Backups, AI datasets, media | Documents, home directories | Databases, VMs |
Challenges of Object Storage
- Latency – Retrieval may be slower for frequently accessed small files.
- Not Ideal for Transactional Workloads – Optimized for read-heavy workloads, not random writes.
- Vendor Lock-In – Dependence on specific cloud providers can reduce flexibility.
- Complex Migration – Moving from file-based to object storage requires planning.
Conclusion
Object storage is a powerful, scalable, and cost-effective solution for managing unstructured data in the cloud. Its flat namespace, metadata-rich architecture, and high durability make it ideal for modern workloads like AI, big data, media storage, and cloud backups.
At Cyfuture AI, we provide secure, scalable object storage solutions tailored for enterprises, developers, and researchers. Our platform ensures high availability, global accessibility, and seamless integration with AI pipelines, generative AI models, and modern applications.
Partner with Cyfuture AI to store and manage your data efficiently while focusing on innovation and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is object storage?
Object storage is a cloud-based storage method that stores
data as discrete objects with metadata and unique identifiers, rather than in a file hierarchy
or blocks.
2. How is object storage different from traditional storage?
Unlike file and block
storage, object storage uses a flat structure, supports metadata-rich objects, and scales
seamlessly for massive datasets.
3. What types of data are best for object storage?
Unstructured data such as images,
videos, backups, logs, AI datasets, and IoT data.
4. Can object storage integrate with AI workflows?
Yes. Object storage is ideal for
storing AI-trained models and datasets used in AI pipelines and inferencing.
5. Why choose Cyfuture AI for object storage?
Cyfuture AI provides secure, scalable,
and globally accessible object storage with seamless integration for AI, media, and cloud-native
workloads.
