Are You Struggling to Choose the Right AI Model for Your Business?
Here's the thing:
In 2026, the AI landscape has evolved into a complex ecosystem where understanding the fundamental differences between model types isn't just academic—it's a competitive necessity.
AI models are fundamentally sophisticated algorithms trained on vast datasets to recognize patterns, make predictions, or generate entirely new content. These systems fall into three primary categories: predictive AI that forecasts outcomes based on historical data, pre-trained models that leverage transfer learning for rapid deployment, and generative AI that creates original content from learned patterns.
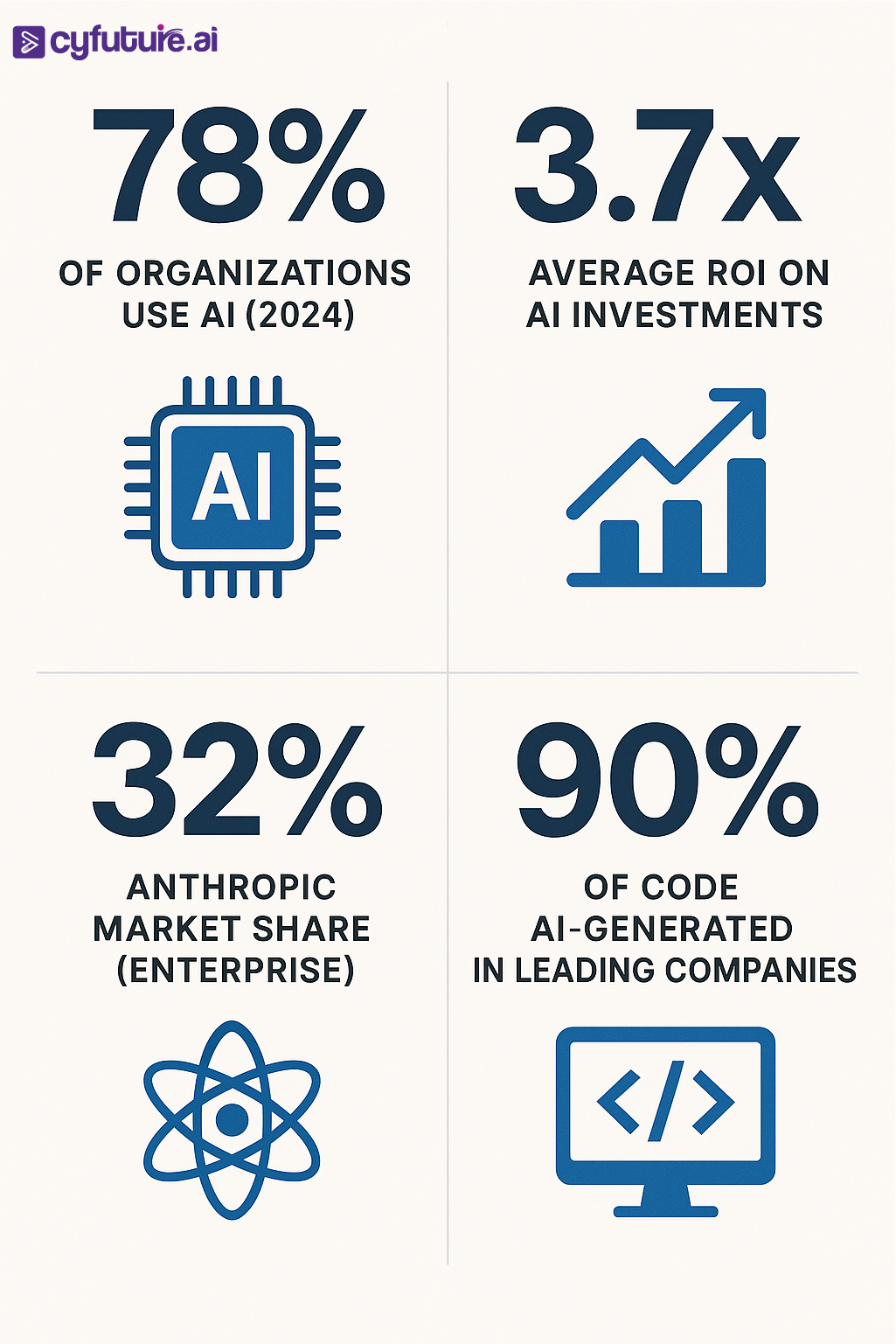
The numbers tell a compelling story. The global AI market reached $391 billion in 2025, with AI expected to contribute $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030. Meanwhile, the generative AI market specifically grew by 76.07% to reach $36 billion by the end of 2025, and 78% of organizations now use AI in at least one business function.
But here's what most enterprises miss:
Not all AI models serve the same purpose, and choosing the wrong approach can cost you millions in wasted resources and missed opportunities.
What Are AI Models?
AI models are mathematical frameworks that process data to learn patterns and make decisions or predictions without explicit programming for each task. Think of them as sophisticated pattern-matching engines that improve through experience.
At their core, these models consist of:
- Architecture: The structural blueprint defining how data flows through the system
- Parameters: Adjustable weights and biases learned during training
- Training data: The information corpus used to teach the model
- Algorithms: The mathematical methods for learning and optimization
The revolution we're witnessing stems from three distinct model approaches, each solving different business challenges. Let's break them down.

Understanding Predictive AI Models
What Makes Predictive AI Different
Predictive AI analyzes historical data to forecast future outcomes. Unlike generative systems that create new content, predictive models identify patterns and project them forward.
The global predictive AI market will grow from $14.9 billion in 2023 to $108 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 21.9%. This growth reflects a fundamental truth: enterprises need reliable forecasting to survive.
Core Mechanisms of Predictive Models
Predictive AI employs several statistical and machine learning techniques:
Regression Analysis: Models linear and non-linear relationships between variables to predict continuous outcomes like sales figures or stock prices.
Classification Algorithms: Categorize data points into discrete classes—spam or not spam, fraudulent or legitimate, high-risk or low-risk customers.
Time Series Forecasting: Analyze sequential data points to predict future trends, essential for demand planning and inventory management.
Clustering Methods: Group similar data points to identify market segments or anomaly detection patterns.
Real-World Applications Driving ROI
Financial institutions lead the charge. In 2025, about 33% of businesses use predictive AI for product recommendations, while among finance teams using AI, 55% rely on it for data analysis, while 47% use it for predictive modeling.
Consider JPMorgan Chase's implementation. The financial giant runs over 300 AI use cases in production, with predictive models detecting fraud patterns in real-time across millions of transactions daily.
Healthcare Applications: Predictive models analyze patient data to forecast disease progression, hospital readmission risks, and treatment outcomes. The value of the global AI in healthcare market size is estimated at $32.3 billion in 2025, with an anticipated 36.4% CAGR from 2025 to 2030.
Manufacturing Optimization: Predictive maintenance systems analyze sensor data to forecast equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime by up to 40%.
Marketing Intelligence: Marketing and sales departments focus 40% more on predictive AI and ML than others, with experts stating AI can potentially result in 50% more sales leads.
Data Quality: The Make-or-Break Factor
Here's the catch:
Predictive AI demands high-quality, accurate training data. Feed it garbage, get garbage predictions. As one Reddit user noted in a discussion on AI model development: "Predictive AI can analyze user behavior on a site and provide suggestions for products they may need, but the accuracy of this data does not necessarily hinder the machine from delivering an answer—that's where it differs from generative approaches."
Cyfuture AI's Predictive Solutions
At Cyfuture AI, we've deployed predictive models that help enterprises achieve 3.7x average ROI on their AI investments. Our predictive analytics platform processes over 10 million data points daily, delivering forecasts with 94% accuracy across retail, finance, and healthcare sectors.
The Power of Pre-Trained Models
Transfer Learning Revolution
Pre-trained models represent a paradigm shift: instead of training from scratch, leverage models already trained on massive datasets and fine-tune them for specific tasks.
Think of it like this:
You wouldn't teach a medical student the entire history of medicine before letting them diagnose patients. Similarly, pre-trained models come with foundational knowledge that you adapt to your specific needs.
The Transformer Architecture Breakthrough
The transformer model, proposed by Google in 2017, has stronger feature extraction capabilities than previous architectures like LSTM. This "Attention Is All You Need" approach revolutionized NLP by enabling parallel processing and better context understanding.
BERT: Bidirectional Understanding
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) changed the game by reading text in both directions simultaneously.
BERT obtains new state-of-the-art results on eleven natural language processing tasks, including pushing the GLUE score to 80.5% (7.7% point absolute improvement).
BERT's architecture:
- 12-24 layers of transformer encoders
- 110M-340M parameters depending on the variant
- Pre-trained on 3.3 billion words from Wikipedia and BookCorpus
Real-World BERT Applications:
- Google Search uses BERT to understand search intent
- Customer service chatbots leverage BERT for sentiment analysis
- Healthcare systems use BERT variants for clinical note analysis
GPT: Generative Pre-Training
While BERT excels at understanding, GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) focuses on generation.
GPT-2 launched by OpenAI has as many as 1.5 billion parameters, trained on an 8 million web page dataset covering diverse topics.
The GPT family evolution:
- GPT: 117M parameters, proved concept viability
- GPT-2: 1.5B parameters, generated coherent multi-paragraph text
- GPT-3: 175B parameters, demonstrated few-shot learning
- GPT-4: Multimodal capabilities, enhanced reasoning
Key Difference: BERT uses a two-way language model for pre-training, while GPT uses an earlier one-way language model, restricting the types of architectures GPT can use.
Read More: Exploring AI Model Libraries: Deploy Smarter with Pre-Trained and Custom Models
Other Notable Pre-Trained Models
RoBERTa: Facebook's robustly optimized BERT approach trained longer on more data.
XLNet: Addresses BERT's limitations by using permutation language modeling.
T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer): Frames all NLP tasks as text-to-text problems, enabling unified handling of translation, summarization, and question answering.
ALBERT: Reduces parameters while maintaining performance through parameter sharing.
Enterprise Adoption Patterns
Organizations achieve 3.7x average ROI on AI investments, with 37% of enterprises using 5+ models in production environments.
The multi-model reality reflects a critical insight: different pre-trained models excel at different tasks. Smart enterprises deploy portfolios:
- GPT-4 for complex reasoning
- Claude for nuanced understanding
- Specialized models for domain-specific applications
Implementation Strategy
Deploying pre-trained models requires understanding:
Fine-Tuning vs. Feature Extraction:
- Fine-tuning: Adjust the pre-trained model's parameters for your specific task
- Feature extraction: Freeze pre-trained layers and add new layers on top
Computational Considerations:
- Pre-trained models reduce training time by 80-95%
- Fine-tuning requires 10-100x less data than training from scratch
- Cloud platforms like Google's Vertex AI and Hugging Face simplify deployment
Generative AI: Creating the Future
Beyond Prediction to Creation
Generative AI doesn't just analyze or predict—it creates entirely new content.
The statistics are staggering:
Goldman Sachs predicts Generative AI will raise global GDP by 7% ($7 trillion), with the generative AI industry expected to create nearly 20 times more revenue in 2032 than it did in 2023.
Over 4 billion prompts are issued daily across major LLM platforms including OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, and Mistral, with ChatGPT reaching 100M+ monthly active users by early 2023.
Core Generative Architectures
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): GANs accounted for over 74% of the generative AI market share in 2023.
GANs consist of two neural networks:
- Generator: Creates synthetic data
- Discriminator: Distinguishes real from fake
They engage in adversarial training—the generator tries to fool the discriminator, which becomes better at detection, forcing the generator to improve. This feedback loop produces remarkably realistic outputs.
Transformer-Based Models: Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini use transformer architecture to generate human-like text.
Diffusion Models: Create images by iteratively denoising random patterns, powering tools like DALL-E, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion.
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): Learn compressed data representations to generate variations, useful for anomaly detection and data augmentation.
Enterprise Adoption: The Reality Check
Here's the uncomfortable truth:
95% of generative AI pilot programs fail to achieve rapid revenue acceleration, with 85-95% failure rates for enterprise implementations. Only 54% of AI models successfully transition from pilot to production.
Yet, companies that moved early saw clear returns with each dollar invested in Gen AI delivering $3.70 back.
Why the disconnect?
Implementation Challenges:
- Data infrastructure inadequacy
- Lack of skilled talent (45% of businesses)
- Security concerns (75% of customers)
- Integration complexity
- Unclear ROI metrics
Breakthrough Use Cases
Code Generation: The killer app. One CTO at a high-growth SaaS company reported that nearly 90% of their code is now AI-generated through Cursor and Claude Code, up from 10-15% twelve months ago with GitHub Copilot.
Content Creation: Seven in 10 marketers expect generative AI will help eliminate busy work and save them five hours of work per week—over a month per year.
Customer Service: Klarna reduced customer support volume by 66% using an AI assistant, while 57% of CX leaders predict chat-based customer support will be significantly influenced by generative AI.
Drug Discovery: Generative models propose entirely new molecular structures, accelerating pharmaceutical development by years.
Synthetic Data Generation: Create training datasets that preserve statistical properties while protecting privacy—critical for healthcare and finance.
Market Leadership Dynamics
The competitive landscape shifted dramatically in 2026:
Anthropic captured 32% of enterprise market share compared to OpenAI's 25% and Google's 20%, with Claude becoming the developer's top choice for code generation at 42% market share.
Model API spending more than doubled, jumping from $3.5 billion to $8.4 billion, marking a shift from model development to production inference.
Also Check: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) in AI: What It Is and Why It Matters
Responsible AI Considerations
As one AI researcher noted on Reddit: "There are copyright issues that high-tech companies built very powerful generative AI models from data that might be copyright-protected. If we want to build more responsible AI models, we should be careful about the quality of the data the models are built with."
Key Challenges:
- Hallucinations: Models confidently generating false information
- Bias amplification: Reflecting and magnifying training data biases
- Copyright concerns: Creating outputs resembling protected material
- Misinformation: Potential for generating misleading content
- Energy consumption: Significant computational requirements
Mitigation Strategies:
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for factual grounding
- Human-in-the-loop validation
- Alignment techniques matching human preferences
- Transparent sourcing and attribution
- Regular bias audits
Cyfuture AI's Generative Solutions
Cyfuture AI has deployed generative models processing over 50 million requests monthly, with enterprise clients achieving 85% faster content creation cycles while maintaining 98% quality standards. Our RAG-enhanced systems reduce hallucinations by 73% compared to baseline models.
Comparing the Three Approaches
When to Use Each Model Type
Predictive AI:
- ✅ Forecasting sales, demand, or market trends
- ✅ Risk assessment and fraud detection
- ✅ Customer churn prediction
- ✅ Maintenance scheduling
- ✅ Investment optimization
Pre-Trained Models:
- ✅ Text classification and sentiment analysis
- ✅ Named entity recognition
- ✅ Question answering systems
- ✅ Language translation
- ✅ Rapid deployment with limited data
Generative AI:
- ✅ Content creation (text, images, code)
- ✅ Product design and prototyping
- ✅ Personalized recommendations
- ✅ Synthetic data generation
- ✅ Creative assistance
Performance Metrics Comparison
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost Considerations
37% of enterprises spend over $250,000 annually on LLMs, with 73% spending over $50,000 yearly.
Organizations invested around $110 million on average for generative AI initiatives in 2024.
Return on investment varies:
- Predictive AI: 6-18 months to ROI
- Pre-trained models: 3-9 months to ROI
- Generative AI: 12-24 months to ROI (when successful)
The Future Landscape
Convergence of Approaches
The lines between model types are blurring. Modern systems combine:
- Predictive models for forecasting
- Pre-trained models for understanding
- Generative capabilities for creation
Example: A customer service system might use predictive AI to forecast inquiry volume, pre-trained models to understand customer intent, and generative AI to draft responses.
Emerging Trends
Agentic AI: 2026 has become known as the "year of agents," with Anthropic leading in training models to iteratively improve responses and integrate tools through Model Context Protocol.
Multimodal Models: Systems processing text, images, audio, and video simultaneously, enabling richer interactions.
Sovereign AI: By 2027, sovereign AI models will be launched in at least 25 countries, with nations building LLMs trained on local languages and values.
Reinforcement Learning: Foundation models are now scaling along a second axis: reinforcement learning with verifiers, beyond just pre-training.
Regulatory Evolution
Global cooperation on AI governance intensified in 2024, with organizations including the OECD, EU, U.N., and African Union releasing frameworks focused on transparency and trustworthiness.
Expect increased focus on:
- Transparency requirements
- Bias auditing mandates
- Data privacy protections
- Environmental impact disclosure
- Copyright frameworks
Economic Impact
AI will contribute more than $15.7 trillion to global GDP by 2030, with generative AI alone expected to drive $1.3 trillion in annual economic impact.
97 million jobs will be created globally due to AI, while 85 million jobs will be displaced, resulting in a net gain of 12 million jobs.
Making Your Move in AI
The AI revolution isn't coming—it's here. The question isn't whether to adopt AI models, but which ones and how quickly.
Key Takeaways:
- Predictive AI delivers reliable forecasting with clear ROI paths, ideal for data-driven decision-making
- Pre-trained models offer rapid deployment and strong performance with transfer learning
- Generative AI unlocks creative possibilities but requires careful implementation
Nearly four out of five organizations are engaging with AI in some form, with just 13% having no adoption plans. The competitive gap is widening—early adopters gain advantages that late movers struggle to close.
Accelerate Your AI Journey With Cyfuture AI
At Cyfuture AI, we've helped over 200 enterprises navigate the AI landscape, deploying solutions that deliver measurable business impact. Our platform-agnostic approach ensures you get the right model for each use case—whether predictive, pre-trained, or generative.
Our clients achieve:
- 3.7x average ROI on AI investments
- 40% reduction in implementation timelines
- 85% faster model-to-production cycles
- 94% forecast accuracy for predictive applications
As a Reddit user insightfully noted: "To get started with generative AI, first focus on areas that can improve human experiences with information."
That's exactly our philosophy—AI should augment human capabilities, not replace human judgment.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What's the fundamental difference between predictive and generative AI?
Predictive AI analyzes historical data to forecast future outcomes (like predicting customer churn or sales trends), while generative AI creates entirely new content (like generating text, images, or code). Predictive AI tells you "what will happen," while generative AI shows you "what could be."
2. Are pre-trained models like BERT and GPT the same?
No. BERT uses bidirectional training to understand context from both directions, making it excellent for classification and comprehension tasks. GPT uses unidirectional training focused on generation, making it better for creating coherent text. BERT is encoder-only, while GPT is decoder-only.
3. How much data do I need to implement these AI models?
It depends on the approach. Predictive AI typically needs thousands of quality examples. Pre-trained models require minimal data for fine-tuning (hundreds to thousands of examples) since they leverage existing knowledge. Generative AI from scratch needs millions or billions of examples, but using pre-trained generative models requires much less.
4. What's the typical ROI timeline for different AI model types?
Predictive AI: 6-18 months; Pre-trained models: 3-9 months; Generative AI: 12-24 months. However, these timelines vary significantly based on implementation complexity, data readiness, and organizational maturity.
5. Can I use multiple AI model types together?
Absolutely. Most successful enterprise implementations use portfolios. For example, a retail system might use predictive AI for inventory forecasting, pre-trained models for customer service chat understanding, and generative AI for personalized product descriptions. 37% of enterprises use 5+ models in production.
6. What are the biggest risks with generative AI?
The primary risks include hallucinations (generating false information), copyright concerns, bias amplification, high computational costs, and security vulnerabilities. Mitigation requires RAG implementations, human oversight, bias audits, and robust security frameworks.
7. How do I choose between building custom models vs. using pre-trained ones?
Use pre-trained models unless you have unique data, specialized requirements, or sufficient resources. Switching between vendors is relatively easy, and most teams upgrade to newer models as they become available. Building from scratch requires millions in investment and months of time.
8. What skills does my team need to implement AI models?
Core skills include: data science and machine learning fundamentals, Python programming, cloud platform knowledge (AWS, Azure, GCP), understanding of model deployment and monitoring, and domain expertise. However, 45% of businesses lack the talent to implement AI effectively, making partnerships with experienced providers crucial.
9. How is AI regulation affecting model implementation?
Global AI governance intensified in 2024, with OECD, EU, U.N., and African Union releasing frameworks focused on transparency and trustworthiness. Expect increasing requirements for model transparency, bias testing, and data protection. Start implementing responsible AI practices now to stay compliant.
Author Bio:
Meghali is a tech-savvy content writer with expertise in AI, Cloud Computing, App Development, and Emerging Technologies. She excels at translating complex technical concepts into clear, engaging, and actionable content for developers, businesses, and tech enthusiasts. Meghali is passionate about helping readers stay informed and make the most of cutting-edge digital solutions.