If you’ve ever wanted to run Python code, train machine learning models, or analyze data without installing anything on your computer, Google Colab is one of the most powerful free tools you can use today.
But despite its popularity, many people still misunderstand what Google Colab actually is, how it works behind the scenes, and how to use it efficiently for real-world projects.
This guide goes beyond surface-level explanations. It walks you through what Google Colab is, how professionals actually use it, its strengths and limitations, and how to get the most value from it—whether you’re a beginner, student, data scientist, or developer.
Table of Contents
- What Is Google Colab?
- Why Google Colab Is So Popular
- How Google Colab Works (Behind the Scenes)
- Getting Started With Google Colab
- Understanding the Google Colab Interface
- Running Python Code in Google Colab
- Using GPUs and TPUs in Google Colab
- Google Colab for Data Science
- Google Colab for Machine Learning & AI
- File Management & Google Drive Integration
- Installing Libraries in Google Colab
- Google Colab Free vs Pro vs Pro+
- Common Google Colab Errors (And How to Fix Them)
- Best Practices for Using Google Colab Efficiently
- Limitations of Google Colab
- Google Colab Alternatives
- Final Thoughts
- FAQs About Google Colab
What Is Google Colab?
Google Colab (short for Colaboratory) is a cloud-based Jupyter Notebook environment provided by Google.
It allows you to:
- Write and execute Python code in your browser
- Use powerful CPUs, GPUs, and TPUs
- Collaborate with others in real time
- Access popular data science and machine learning libraries instantly
The most important thing to understand is this:
Google Colab runs your code on Google’s servers — not on your local machine.
That single fact explains why Colab is so fast, accessible, and widely used.
Why Google Colab Is So Popular
Google Colab didn’t become popular by accident. It solves several real problems at once.
Key Reasons People Use Google Colab
- No installation required
- Free access to GPUs
- Works on any device with a browser
- Pre-installed ML & data science libraries
- Easy sharing and collaboration
For students, Colab removes hardware barriers.
For professionals, it speeds up experimentation.
For teams, it enables frictionless collaboration.
How Google Colab Works (Behind the Scenes)
When you open a Colab notebook, you’re connecting to a temporary virtual machine hosted by Google.
This VM includes:
- A Linux operating system
- Python pre-installed
- Common libraries like NumPy, Pandas, TensorFlow, PyTorch
Important details most guides don’t explain clearly:
- Sessions are temporary
- Files stored locally disappear when the runtime resets
- Resource availability varies depending on demand
Understanding this helps avoid frustration later.
Getting Started With Google Colab
Getting started is extremely simple:
- Open Google Colab
- Sign in with your Google account
- Click New Notebook
- Start writing Python code
No setup. No configuration. No environment conflicts.
That ease of entry is one of Colab’s biggest strengths.
Understanding the Google Colab Interface
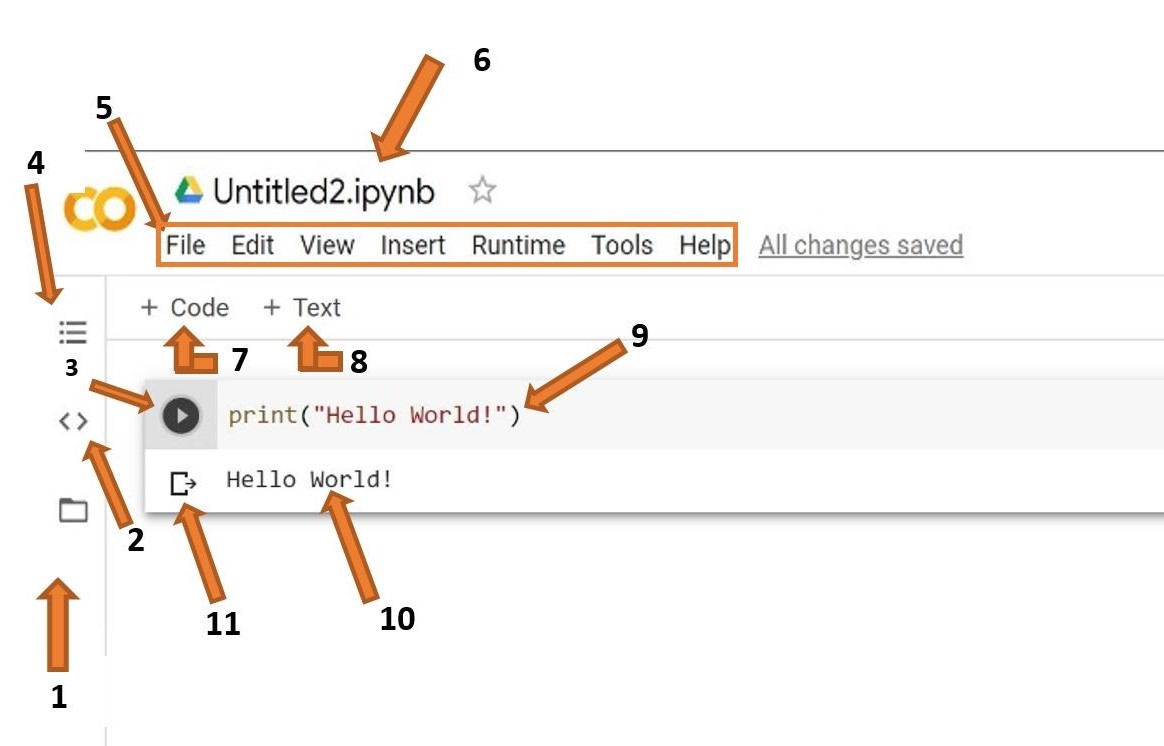
At first glance, Colab looks like a standard Jupyter Notebook — but with important enhancements.
Main Components
- Code cells – Execute Python code
- Text cells – Markdown documentation
- Runtime menu – Control execution environment
- Files pane – View runtime file system
Colab also autosaves notebooks directly to Google Drive, which removes the fear of losing work.
Running Python Code in Google Colab
Running Python in Colab feels instant because the environment is already prepared.
You can:
- Execute code cell-by-cell
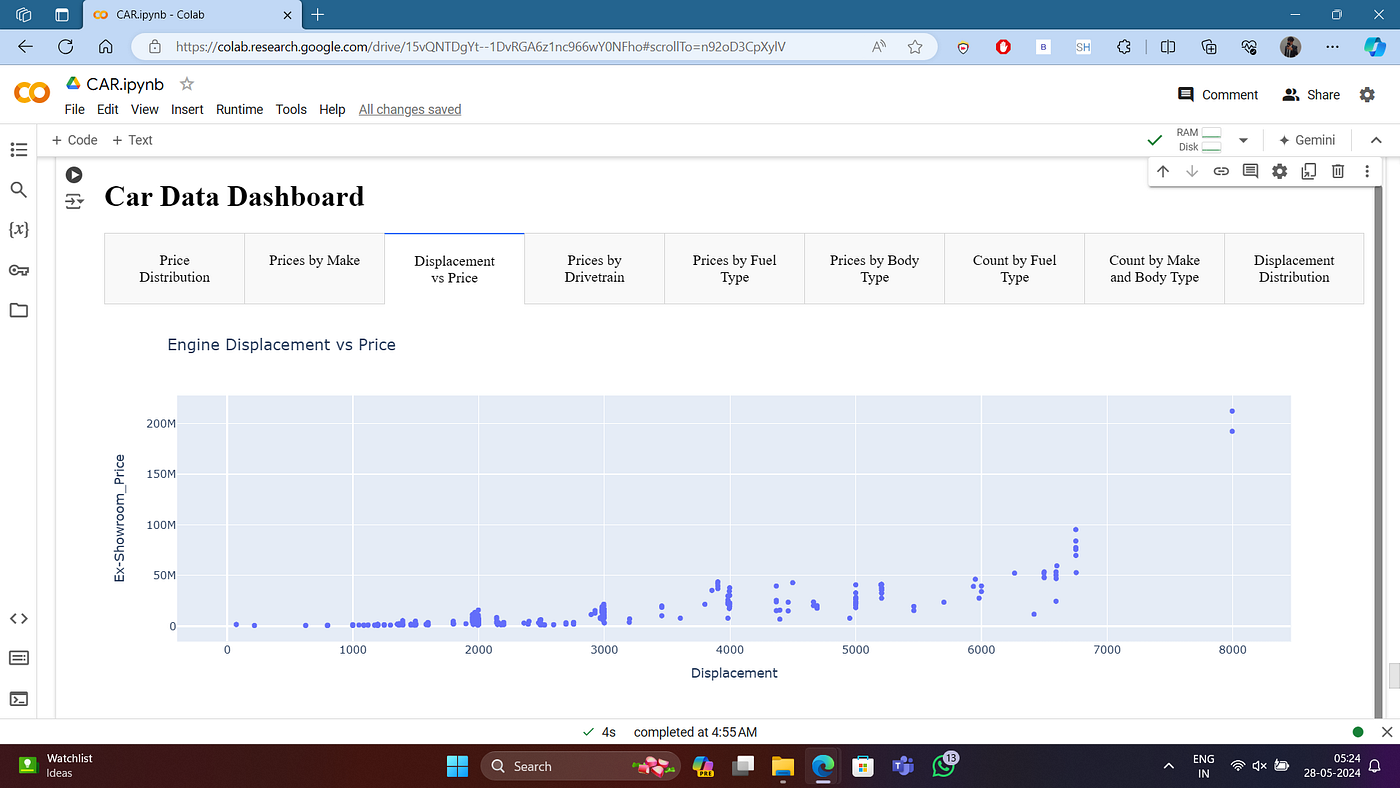
- Visualize plots inline
- Display images, tables, and outputs
Colab supports:
- Standard Python
- IPython magic commands
- Shell commands using !
This makes it extremely flexible for experimentation.
Using GPUs and TPUs in Google Colab
One of the biggest advantages of Colab is access to hardware acceleration.
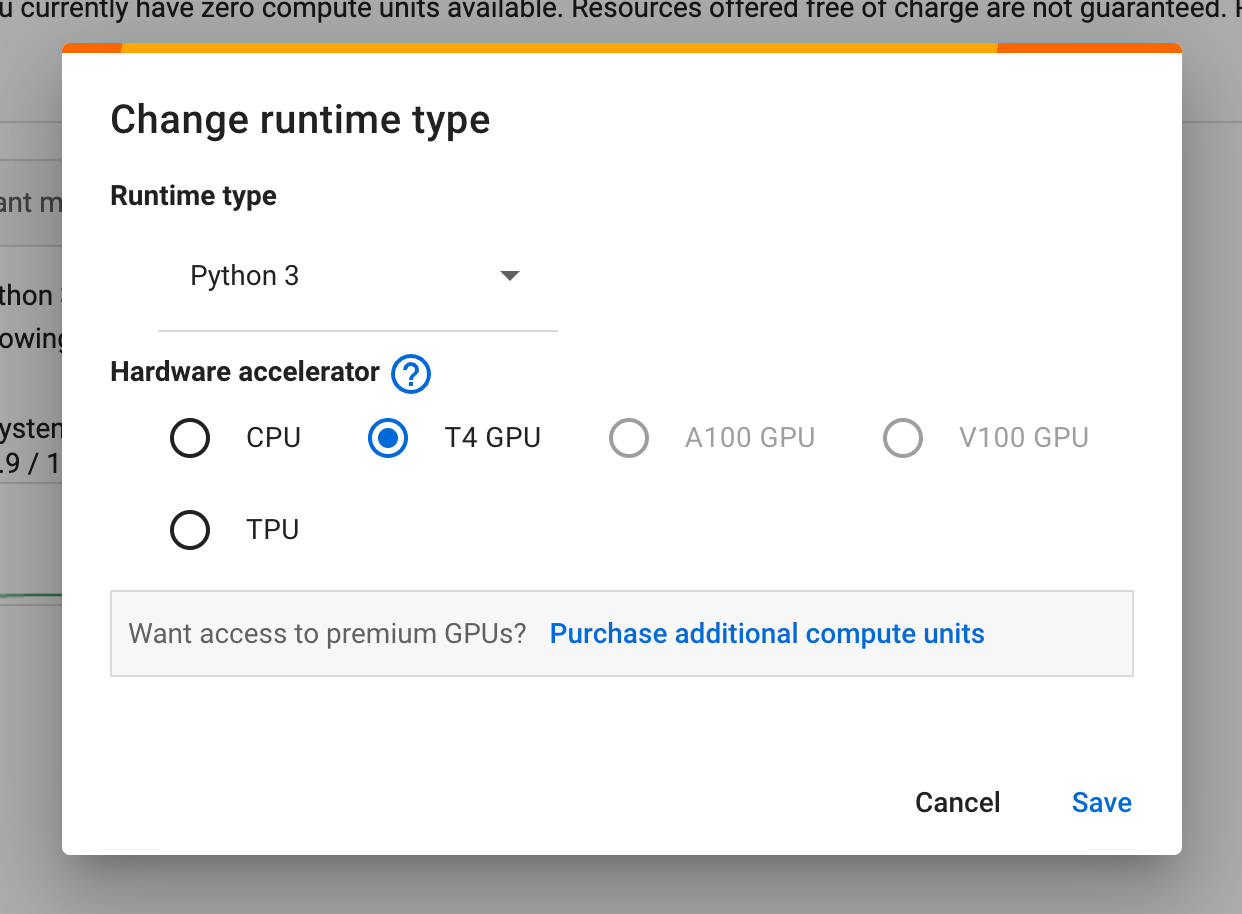
Available Options
- CPU (default)
- GPU
- TPU (limited but powerful)
You can enable these from:
Runtime → Change runtime type
This is why Colab is heavily used for:
- Deep learning
- Neural network training
- Computer vision
- NLP models
Google Colab for Data Science
Data scientists use Colab for:
- Exploratory data analysis (EDA)
- Data cleaning
- Visualization
- Rapid prototyping
Popular libraries work out of the box:
- Pandas
- NumPy
- Matplotlib
- Seaborn
Colab is especially useful for sharing notebooks with stakeholders, since results and explanations live in one place.
Google Colab for Machine Learning & AI
Google Colab is widely used for:
- Model training
- Hyperparameter tuning
- Experiment tracking
- Educational demos
Frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch are pre-installed, saving hours of setup time.
For learning an AI model, Colab removes the most common blocker: hardware limitations.
File Management & Google Drive Integration
Colab integrates deeply with Google Drive.
You can:
- Mount Drive to access persistent files
- Read and write datasets directly
- Share notebooks like Google Docs
This is essential because local runtime storage is temporary.
Installing Libraries in Google Colab
Even though many libraries are pre-installed, you can install others easily.
Colab allows:
- pip install
- apt-get
- Custom GitHub installations
Keep in mind:
- Installed libraries reset when the runtime restarts
- Pin versions for reproducibility
Google Colab Free vs Pro vs Pro+
Google offers multiple tiers:
Free
- Limited runtime
- Shared resources
- Occasional disconnects
Pro
- Longer runtimes
- Faster GPUs
- Higher priority access
Pro+
- Maximum resource availability
- Best for heavy workloads
Most beginners and learners are well served by the free tier.
Common Google Colab Errors (And How to Fix Them)
Some frequent issues include:
- Runtime disconnects
- Memory crashes
- Library conflicts
- GPU not available
Most problems are solved by:
- Restarting runtime
- Clearing outputs
- Switching hardware type
- Using smaller datasets
Understanding Colab’s temporary nature helps avoid panic.
Best Practices for Using Google Colab Efficiently
- Save outputs to Drive
- Use checkpoints for models
- Comment notebooks clearly
- Avoid long idle sessions
- Monitor RAM and disk usage
Treat Colab as an experimental workspace, not long-term storage.
Limitations of Google Colab
Despite its strengths, Colab is not perfect.
Key Limitations
- Session time limits
- No guaranteed hardware
- Not ideal for production
- Internet dependency
Colab is best used for development, learning, and experimentation—not deployment.
Google Colab Alternatives
Depending on your needs, alternatives include:
- Local Jupyter Notebook
- Kaggle Notebooks
- Cloud VM setups
- Paid ML platforms
Each option has trade-offs between control, cost, and convenience.
Final Thoughts
Google Colab has changed how people learn, experiment, and collaborate with Python and machine learning.
Its real value isn’t just free GPUs — it’s accessibility.
By removing setup friction, Colab allows people to focus on thinking, building, and learning, instead of troubleshooting environments.
If you’re serious about data science, machine learning, or Python development, Google Colab is not just a tool — it’s a skill worth mastering.
FAQs About Google Colab
What is Google Colab used for?
Google Colab is used to write and run Python code in a web browser without installing anything locally. It’s commonly used for data analysis, machine learning, deep learning, education, and quick experimentation with code.
Is Google Colab free to use?
Yes, Google Colab offers a free tier that includes access to CPUs and limited GPU usage. There are also paid plans (Pro and Pro+) that provide longer runtimes, faster hardware, and higher resource priority.
Do I need to install Python to use Google Colab?
No. Google Colab runs Python on cloud-based virtual machines, so you don’t need to install Python or any libraries on your computer. Everything runs directly in your browser.
How long can a Google Colab session run?
Google Colab sessions are temporary. Free users typically get sessions lasting up to 12 hours, though runtimes can disconnect earlier due to inactivity or resource limits.
Does Google Colab save files automatically?
Colab notebooks are automatically saved to Google Drive, but files created inside the runtime storage are temporary. To keep data permanently, you should save files to Google Drive or download them locally.
Can Google Colab use GPUs and TPUs?
Yes. Google Colab allows users to enable GPUs and TPUs for faster computation, especially for machine learning and deep learning tasks. Availability depends on usage limits and current demand.
Is Google Colab good for beginners?
Yes, Google Colab is beginner-friendly because it removes setup complexity. Beginners can focus on learning Python, data science, or machine learning without worrying about environment configuration.
What are the limitations of Google Colab?
Google Colab has runtime time limits, limited RAM and disk space, no guaranteed hardware availability, and is not designed for production deployment. It is best used for learning, experimentation, and development.
Can Google Colab replace a local Jupyter Notebook?
For many tasks like learning, prototyping, and lightweight model training, Google Colab can replace a local Jupyter Notebook. However, for offline work or production workflows, a local setup is often better.
Is Google Colab safe for sensitive data?
Google Colab is secure for general use, but it’s not recommended to upload highly sensitive or confidential data unless you fully understand Google’s data handling and access controls.
