GPU as a Service (GPUaaS) has quietly become one of the most critical layers of modern computing.
If you work in AI, machine learning, data science, rendering, or high-performance computing, chances are your biggest bottleneck isn’t talent or ideas - it’s compute. GPUs are expensive, hard to source, and painfully easy to underutilize when owned outright.
GPUaaS exists to solve exactly that problem.
Instead of buying GPUs that age quickly and sit idle, organizations can rent powerful GPUs on demand, scale instantly, and pay only for what they actually use. This shift has fundamentally changed how AI systems are built, tested, and deployed.
This guide goes far beyond surface-level definitions. It explains how GPUaaS works in practice, who should use it (and who shouldn’t), compares the top GPUaaS providers with real pricing, and helps you make smarter decisions without getting trapped in cloud complexity.
Table of Contents
- What Is GPU as a Service?
- How GPUaaS Works Behind the Scenes
- Why GPUaaS Is Critical for AI & ML
- GPUaaS vs On-Prem GPUs vs Cloud VMs
- Real-World GPUaaS Use Cases
- GPUaaS Architecture Explained
- GPU Pricing Models & Cost Optimization
- Top 10 GPUaaS Providers (Detailed)
- GPUaaS Pricing Comparison (Hourly)
- Performance, Security & Compliance
- Common GPUaaS Mistakes
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What Is GPU as a Service?
GPU as a Service (GPUaaS) is a cloud computing model where graphics processing units (GPUs) are delivered as on-demand infrastructure over the internet.
Instead of owning physical GPU servers, teams can:
- Provision GPUs in minutes
- Scale up or down instantly
- Access enterprise-grade NVIDIA hardware remotely
- Pay only for usage time
GPUaaS is widely used for:
- AI and ML training
- AI inference
- Deep learning research
- Video rendering and animation
- Scientific simulations
- Financial modeling
At its core, GPUaaS removes hardware ownership friction while giving teams access to cutting-edge acceleration.
How GPUaaS Works Behind the Scenes
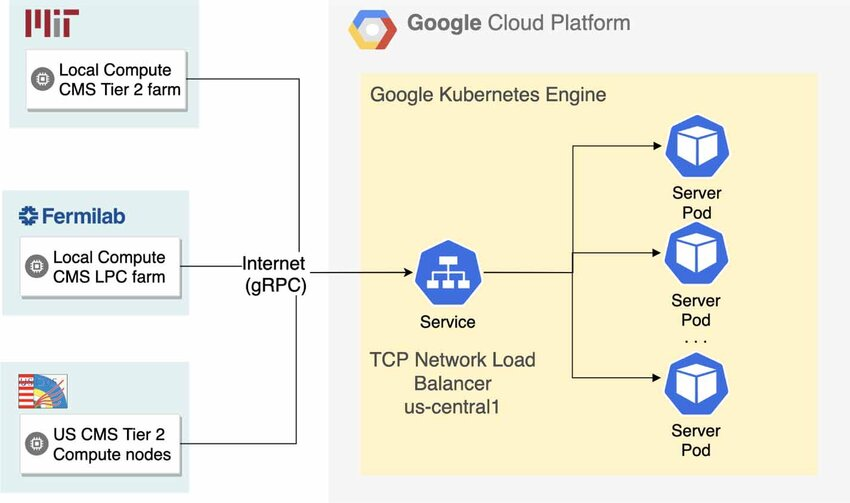

Behind every GPUaaS platform is a large data center filled with high-performance GPUs.
Typical workflow:
- A user requests a GPU instance
- The cloud orchestrator assigns a physical GPU
- A virtual machine or container launches
- CUDA drivers and libraries are preinstalled
- Workloads run remotely with near-native performance
Most GPUaaS platforms integrate with:
- PyTorch
- TensorFlow
- CUDA
- Kubernetes
This allows teams to focus on models and results, not hardware maintenance.
Why GPUaaS Is Critical for AI & ML
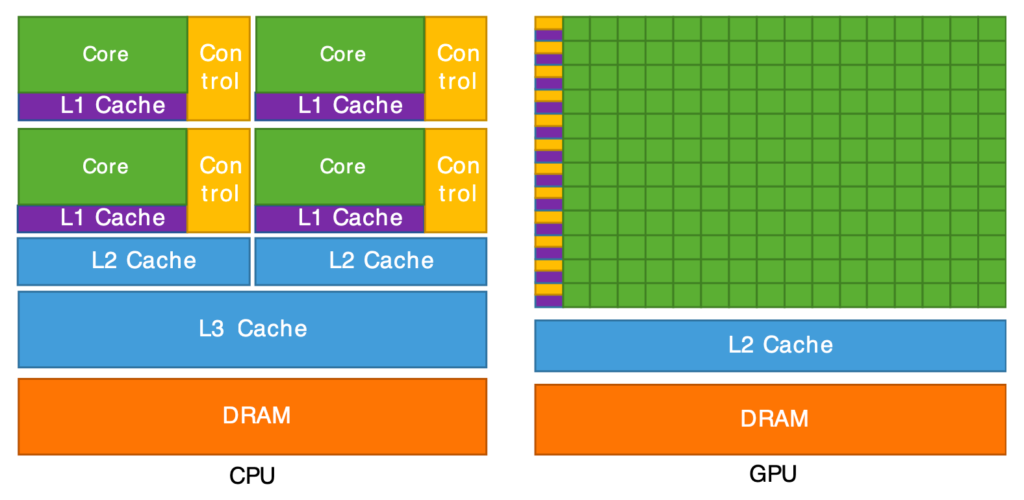
Modern AI workloads are not practical on CPUs alone.
GPUs excel at:
- Parallel computation
- Matrix multiplication
- Vectorized operations
Training a large neural network on CPUs can take weeks or months. GPUs reduce this to hours or days.
GPUaaS solves three major challenges:
- Cost barrier – No upfront capital expenditure
- Scalability – Scale from 1 GPU to dozens instantly
- Accessibility – Startups access enterprise-grade hardware
GPUaaS vs On-Prem GPUs vs Cloud VMs
|
Feature |
GPUaaS |
On-Prem GPUs |
Standard Cloud VMs |
|
Upfront cost |
None |
Very high |
Low |
|
Scalability |
Instant |
Limited |
Moderate |
|
Maintenance |
Provider |
You |
Provider |
|
AI performance |
High |
High |
Low |
|
Flexibility |
Very high |
Low |
Medium |
GPUaaS is ideal for bursty, experimental, or fast-growing workloads.
Real-World GPUaaS Use Cases

AI & Machine Learning
- Model training and fine-tuning
- Hyperparameter optimization
- Large language models (LLMs)
- Computer vision and NLP
Data Science
- Large dataset processing
- Feature engineering
- Simulation workloads
Media & Rendering
- Video encoding
- 3D rendering
- Animation pipelines
Scientific Research
- Climate modeling
- Genomics and molecular simulations
- Physics and engineering computation
FinTech
- Fraud detection
- Risk modeling
- Monte Carlo simulations
- Algorithmic trading
GPUaaS Architecture Explained
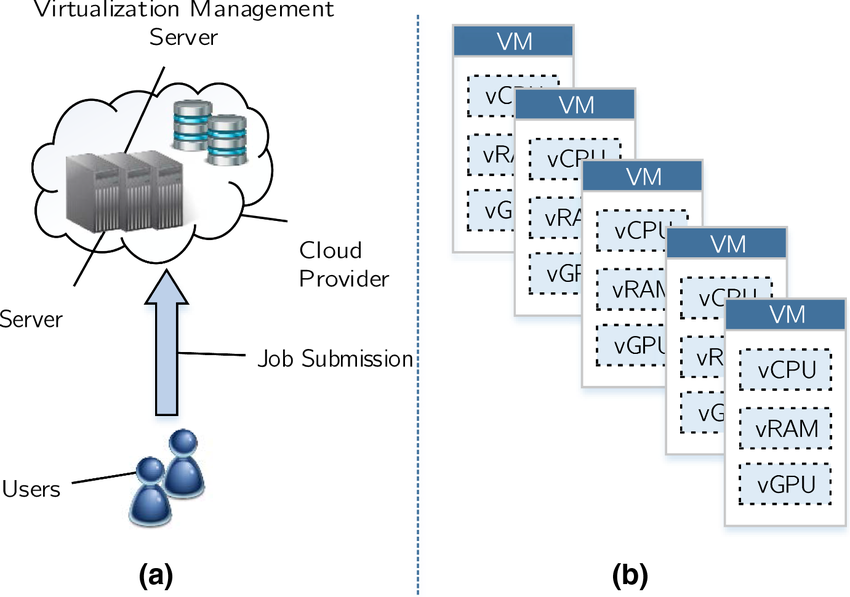

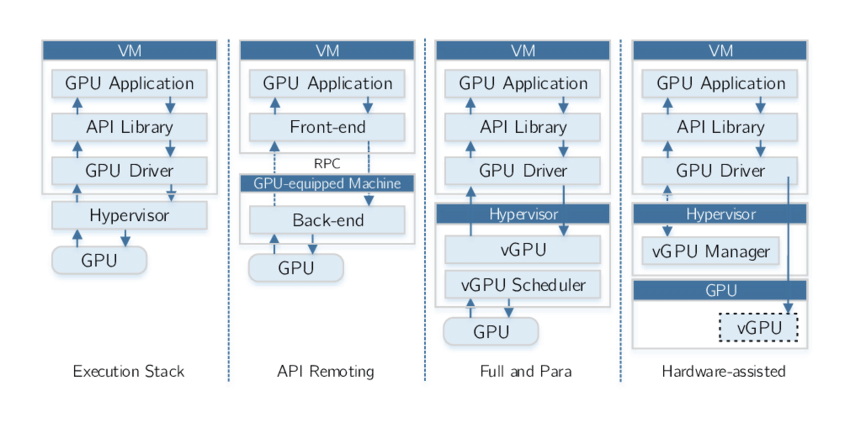
A typical GPUaaS stack includes:
- Physical GPU nodes
- Hypervisors or container runtimes
- GPU passthrough or virtualization
- High-speed networking
- Monitoring and billing layers
Some providers offer bare-metal GPUs for maximum performance; others offer shared GPUs for cost efficiency.
GPU Pricing Models & Cost Optimization
Common pricing models
- Hourly billing
- Per-second billing
- Reserved instances
- Spot / preemptible GPUs
Optimization tips
- Use spot GPUs for training
- Shut down idle instances
- Separate training and inference
- Monitor GPU utilization weekly
Top 10 GPUaaS Providers Explained (Real Strengths, Real Trade-offs)
Choosing a GPUaaS provider is not about picking the biggest brand.
It’s about availability, pricing clarity, performance consistency, and how much friction you’re willing to tolerate.
Below is a clear, honest breakdown of the top GPUaaS providers - who they’re really for, where they shine, and where they fall short.


1. Cyfuture AI (Best Overall GPUaaS)
Best for: Enterprises, AI startups scaling to production, regulated workloads
Cyfuture AI is purpose-built specifically for GPU workloads, not a general cloud that later “added GPUs.” This is a critical distinction.
Where hyperscalers optimize for thousands of services, Cyfuture AI optimizes for GPU availability, performance, and predictability. That makes it especially attractive for teams that cannot afford GPU shortages, surprise pricing, or noisy neighbors.
What Cyfuture AI does exceptionally well
- Dedicated NVIDIA GPUs (A100, H100, H200 series)
- Predictable, transparent pricing
- High GPU availability even during global shortages
- Bare-metal and virtualized GPU options
- Strong enterprise security and compliance posture
Where it may not fit
- Teams looking for dozens of non-GPU cloud services in one platform
Why it ranks #1:
Cyfuture AI delivers the best balance of cost, performance, reliability, and simplicity for real-world AI workloads.
2. CoreWeave
Best for: Large-scale AI training, LLMs, multi-GPU clusters
CoreWeave is a GPU-native cloud designed for organizations that need a lot of GPUs at the same time.
It’s especially popular with companies training large language models or running massive distributed workloads. CoreWeave’s infrastructure is optimized for dense GPU clusters, fast networking, and Kubernetes-based orchestration.
Strengths
- Extremely high GPU availability
- Excellent for multi-node training
- Strong container and Kubernetes support
Limitations
- Pricing favors volume commitments
- Less friendly for small teams or short jobs
Bottom line:
CoreWeave is ideal when scale matters more than flexibility.
3. Lambda Labs
Best for: ML engineers, research teams, startups
Lambda Labs has built a strong reputation in the ML community by focusing on developer experience.
Their GPU cloud is straightforward, well-documented, and optimized for popular frameworks like PyTorch and TensorFlow. Many researchers and startups choose Lambda because it feels designed by ML practitioners, not enterprise sales teams.
Strengths
- Competitive GPU pricing
- Simple onboarding
- ML-first tooling
- Strong documentation
Limitations
- Fewer enterprise governance controls
- Limited global regions compared to hyperscalers
Bottom line:
Lambda Labs is a great choice for teams that want speed and simplicity without hyperscaler complexity.
4. RunPod
Best for: Cost-sensitive training, experimentation, burst workloads
RunPod is known for its aggressive pricing, especially through spot and community-hosted GPUs.
It’s widely used by independent researchers, hobbyists, and early-stage startups that need GPU power cheaply and quickly, without long-term commitments.
Strengths
- Very low-cost spot GPUs
- Wide variety of GPU models
- Fast spin-up times
Limitations
- Less predictable uptime
- Not ideal for production or regulated workloads
Bottom line:
RunPod is excellent for experimentation and training, but risky for mission-critical systems.
5. Paperspace
Best for: Prototyping, learning, demos
Paperspace focuses heavily on ease of use. Its UI is beginner-friendly, and it’s often used by people new to GPUs or ML workflows.
It works well for proof-of-concepts, demos, and early experimentation, but is less competitive at scale.
Strengths
- Very easy onboarding
- Clean user interface
- Good for RTX-based workloads
Limitations
- Pricing higher than newer GPUaaS providers
- Limited enterprise scalability
Bottom line:
Paperspace is ideal for getting started, not for long-term production workloads.
6. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Best for: Enterprises already fully invested in AWS
AWS offers GPUs through EC2, SageMaker, and other services. While powerful, AWS GPUs are notoriously expensive and often hard to procure during peak demand.
Most teams choose AWS GPUs not because they’re the best, but because they’re already locked into the AWS ecosystem.
Strengths
- Deep enterprise integrations
- Extensive compliance certifications
- Massive global footprint
Limitations
- 2–3× higher GPU costs
- Complex pricing
- GPU availability constraints
Bottom line:
AWS GPUs make sense only if ecosystem integration outweighs cost concerns.
7. Google Cloud
Best for: Teams using Google’s AI stack
Google Cloud excels in AI tooling, especially for teams leveraging TensorFlow or Google’s managed ML services.
However, GPU pricing remains high, and availability can be inconsistent.
Strengths
- Strong ML tooling
- TPU alternatives
- Clean infrastructure design
Limitations
- Expensive GPUs
- Less flexible pricing models
Bottom line:
Google Cloud is powerful, but not cost-efficient for GPU-heavy workloads.
8. Microsoft Azure
Best for: Enterprises using Microsoft ecosystems
Azure GPUs integrate well with Microsoft’s enterprise stack, including Active Directory and compliance frameworks.
Provisioning GPUs, however, can be slower, and pricing is often higher than specialized GPUaaS providers.
Strengths
- Strong enterprise compliance
- Microsoft ecosystem integration
Limitations
- Slower GPU provisioning
- High pricing
- Less GPU specialization
Bottom line:
Azure GPUs work best when compliance and enterprise integration matter more than speed or cost.
9. OVHcloud
Best for: European workloads, data residency requirements
OVHcloud is popular in Europe due to data sovereignty and competitive pricing compared to hyperscalers.
GPU availability is more limited, but pricing is often attractive for mid-sized workloads.
Strengths
- EU data residency
- Competitive pricing
- Simple billing
Limitations
- Limited GPU model selection
- Smaller ecosystem
Bottom line:
OVHcloud is a strong option for EU-focused GPU workloads.
10. Vultr
Best for: Small workloads, inference, edge use cases
Vultr offers simple GPU instances with transparent pricing, but does not compete at the high end of AI training.
Strengths
- Simple pricing
- Easy deployment
- Good for inference
Limitations
- Limited high-end GPUs
- Not suitable for large training jobs
Bottom line:
Vultr is best for light GPU use, not heavy AI training.
GPUaaS Provider Pricing Comparison (Hourly)
Pricing transparency note:
These are typical on-demand hourly ranges observed in 2024–2025. Actual pricing varies by region and availability.
|
Provider |
A100 (40GB) |
H100 |
H200 |
GPU Availability |
Best For |
Key Strength |
|
Cyfuture AI |
$1.9–$2.3 |
$2.39–$6.0 |
$6.5–$8.0 |
Very High |
Production AI, enterprises |
Predictable pricing & availability |
|
CoreWeave |
$2.2–$2.9 |
$5.5–$7.0 |
$7.0–$9.0 |
Very High |
Large LLM training |
Massive GPU clusters |
|
Lambda Labs |
$1.99–$2.49 |
$4.99–$6.99 |
Limited |
Medium |
ML research teams |
Developer-friendly setup |
|
RunPod |
$1.2–$2.0 |
$4.0–$6.5 |
Limited |
Medium |
Experiments, training jobs |
Lowest spot pricing |
|
Paperspace |
$2.1–$3.0 |
Limited |
Not Available |
Low |
Prototyping |
Simple onboarding |
|
AWS |
$4.1–$4.9 |
$9–$12 |
$12–$15+ |
Low–Medium |
Enterprise ecosystems |
Deep cloud integration |
|
Google Cloud |
$3.8–$4.6 |
$8.5–$11 |
$11–$14+ |
Low–Medium |
Google AI stack users |
TPU + AI tooling |
|
Azure |
$4.2–$5.0 |
$9.5–$13 |
$12–$16+ |
Low |
Regulated enterprises |
Compliance & governance |
|
OVHcloud |
$1.8–$2.5 |
Limited |
Not Available |
Medium |
EU workloads |
Data residency |
|
Vultr |
Limited |
Limited |
Not Available |
Low |
Inference & small workloads |
Simple pricing |
Performance, Security & Compliance
Performance
- GPU type matters more than count
- Network bandwidth affects distributed training
- Storage I/O can bottleneck jobs
Security
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- Isolated GPU access
- Secure VM/container boundaries
Compliance
Many providers support:
- SOC 2
- ISO 27001
- HIPAA
- GDPR
Common GPUaaS Mistakes
- Over-provisioning GPUs
- Leaving instances idle
- Using GPUs for CPU-bound tasks
- Ignoring data transfer costs
- Choosing providers by brand alone
Conclusion:
GPU as a Service is no longer an optional convenience or a short term workaround. It has become core infrastructure for organizations building, training, and deploying modern AI, machine learning, and high performance workloads.
As this guide shows, the challenge today is not access to GPUs. It is access to the right GPUs at the right time with predictable cost and performance. Owning hardware often leads to underutilization, long upgrade cycles, and high operational overhead. GPUaaS removes these constraints by aligning compute capacity directly with real workload demand.
One of the most important takeaways is that not all GPUaaS providers deliver the same experience.
While hyperscalers offer broad ecosystems, they often come with higher costs, complex pricing, and limited GPU availability. In contrast, purpose built GPUaaS platforms focus specifically on performance, availability, and simplicity. Providers like Cyfuture AI stand out by prioritizing dedicated GPU access, transparent pricing, and enterprise grade reliability, making them well suited for production AI workloads where consistency and predictability matter.
The most successful teams do not choose GPUaaS based on brand recognition alone. They evaluate GPU availability during peak demand, cost to performance efficiency, scalability without friction, security and compliance readiness, and long term operational simplicity.
In the end, winning with GPUaaS is not about running the most GPUs. It is about using the right GPUs only when you need them on a platform that will not slow you down.
For organizations serious about AI and accelerated computing, GPUaaS is no longer just the most practical path forward. It is the path that keeps you competitive.
FAQs:
1. What is GPU as a Service (GPUaaS)?
GPU as a Service is a cloud computing model that provides on-demand access to GPUs without owning physical hardware. Users can scale GPU resources up or down and pay only for actual usage.
2. How does GPUaaS work?
GPUaaS works by allocating physical GPUs from a provider’s data center to virtual machines or containers. The GPUs are preconfigured with drivers and frameworks, allowing workloads to run remotely with near-native performance.
3. What is GPUaaS used for?
GPUaaS is commonly used for AI and machine learning training, deep learning, data science, video rendering, scientific simulations, and financial modeling.
4. Is GPU as a Service cheaper than buying GPUs?
GPUaaS is often cheaper for variable or burst workloads because it eliminates upfront hardware costs, maintenance, and idle resource waste. For constant 24/7 usage, on-prem GPUs may be more cost-effective.
5. Is GPUaaS suitable for startups?
Yes. GPUaaS allows startups to access enterprise-grade GPUs without capital investment, making it ideal for experimentation, rapid scaling, and MVP development.
6. Can GPUaaS be used for inference as well as training?
Yes. Many organizations use GPUaaS for both model training and real-time inference, often separating environments to optimize cost and performance.
7. What is the difference between GPUaaS and cloud GPU instances?
GPUaaS focuses specifically on GPU performance, availability, and pricing simplicity, while cloud GPU instances are part of larger cloud ecosystems with more complexity and higher costs.
8. Is GPUaaS better than AWS for AI workloads?
GPUaaS providers are often more cost-effective and offer better GPU availability for AI workloads compared to AWS, which is more expensive but offers deeper enterprise integrations.
9. How much does GPU as a Service cost?
GPUaaS pricing typically ranges from under $1/hour for RTX GPUs to $5–$6/hour for high-end GPUs like the NVIDIA H100, depending on provider, region, and availability.
10. Which industries benefit most from GPUaaS?
Industries that benefit most include artificial intelligence, healthcare, finance, media and entertainment, scientific research, and autonomous systems.


